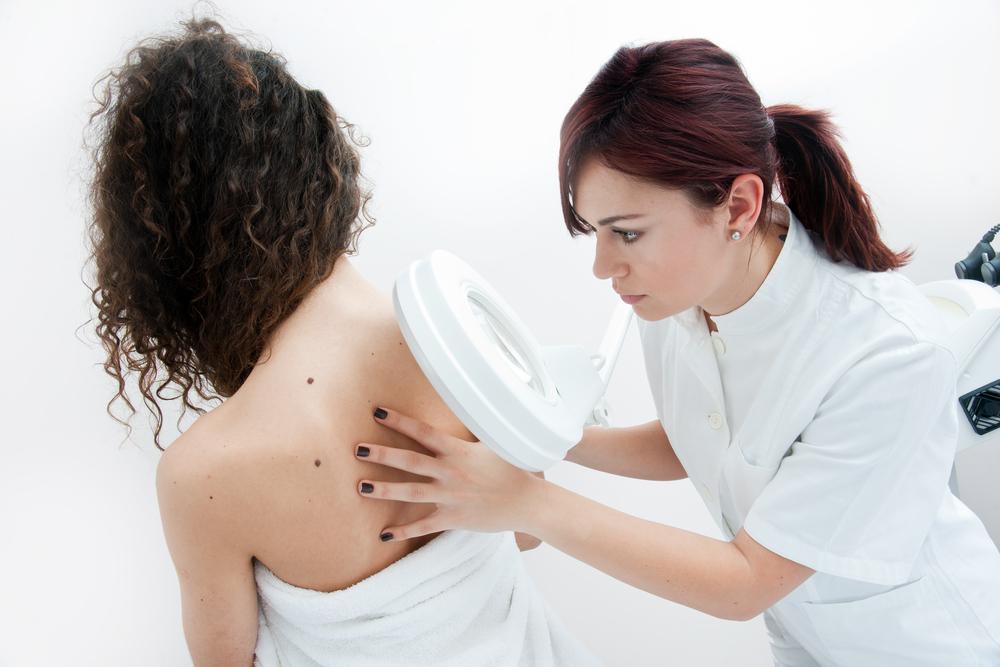
Important facts on skin cancer
Skin cancer is the term referring to cancer of the skin, which is the abnormal and uncontrolled growth of skin cells. As per the World Health Organisation, one in every three cancer cases that are diagnosed is found to be of skin cancer which makes it one of the most common cancers.
Types and symptoms of skin cancer
Skin cancer is categorized based on the type of skin cells that are affected. There are two basic categories of skin cancers; non-melanomas and melanomas. Non-melanoma cancers are basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. Melanomas usually originate from the pigment-producing melanocytes in the skin. The symptoms of non-melanoma skin cancer are usually a non-healing open wound on the skin or the change in shape, size, color or texture of a mole or any other skin growth. Melanoma cancers have more symptoms that are usually referred to by the mnemonic ABCDE which signify asymmetry, irregular borders, changes in color, diameter larger than a pencil eraser, and evolution of a mole’s characteristics.
Causes and risk factors
The main risk factor is the damage caused to the skin by harmful UV radiation in sunlight. People with a history of excessive sun exposure and/or sunburns are more predisposed to this type of cancer. People with light skin, hair, and eyes are at a higher risk of getting this type of cancer. Warmer climates and higher altitudes also cause higher exposure to UV radiation. Non-melanoma cancers are also seen more in adults who are 50 years or older.
People with a family history of immediate relatives, who have had some form of skin cancer are 50% more likely to develop melanoma than the others. People who have a history of non-melanoma type of skin cancer and those with a compromised immune system are at a higher risk of having melanoma. People with pigment disorders such as albinism are also prone to melanoma. Ongoing research has identified gene mutations are responsible for a person to be more prone to these types of cancer.
Stages
Localized melanomas that have not gone below the outer layer are classified as stage 0, and cancers that have penetrated below the epidermis into the dermis, but have no other risky traits are called stage 1. Stage 2 is localized, but have other traits with risks of spreading. Stage 3 and 4 melanomas are those that have spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment
Treatment of skin cancer usually involves surgical removal of the tumor site by surgical excision or Mohs Micrographic Surgery. For skin cancers that are in stage 3 and 4, further therapy such as immunotherapy, radiation therapy, laser therapy, targeted therapy, and chemotherapy, are also recommended.
Prevention
The basic concept behind the prevention of skin cancer is to protect one’s skin from harmful UV radiation by wearing sunscreen, proper clothing, sunglasses as well as hats, avoiding the sun between 10 am and 4 pm and avoiding skin tanning both naturally and artificially.